Discovering Europe through a Physical Map
Maps are a crucial instrument for geographers, travelers, and cartographers, enabling us to comprehend our surroundings, venture into new areas, and traverse unfamiliar territories. Among various map types, each serving a unique purpose, physical maps and political maps are quite prevalent. This article will hone in on the physical map of Europe, elaborating on its distinctions from political maps.
Understanding Physical Maps of Europe
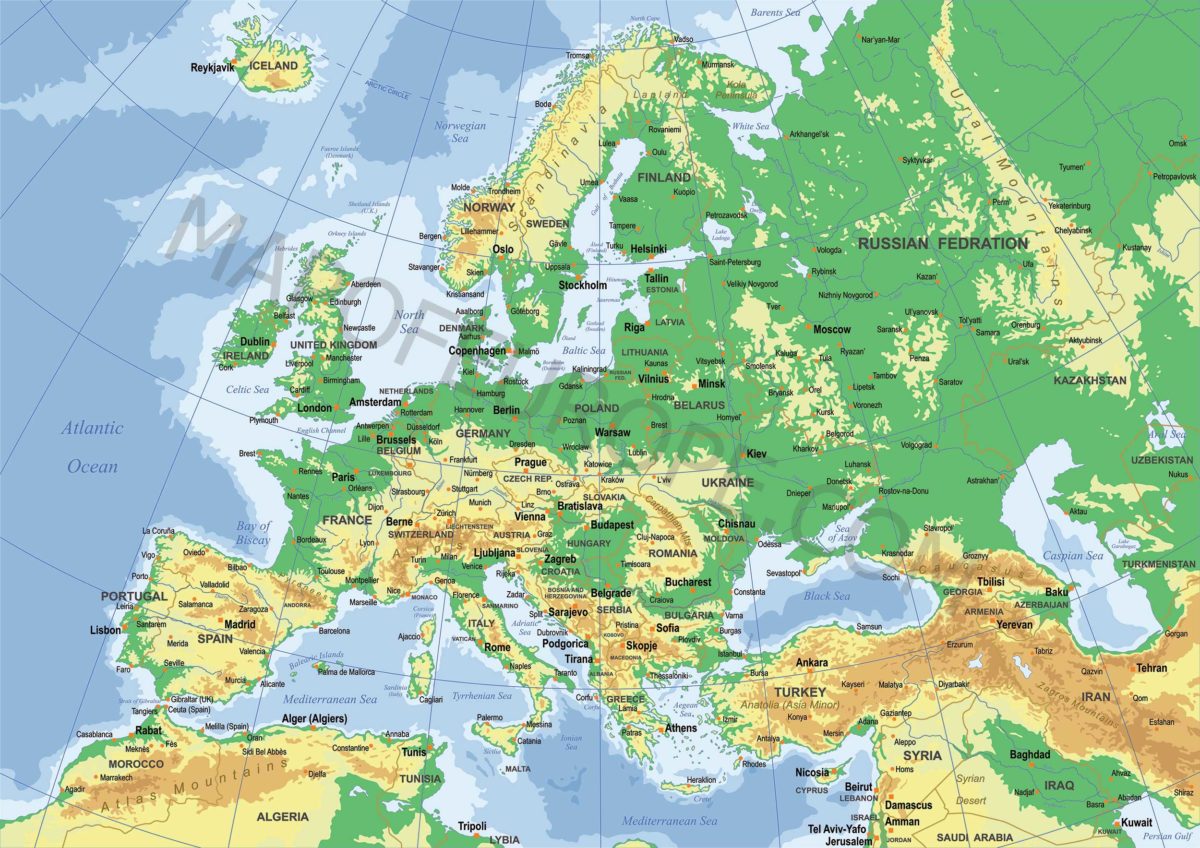
A physical map of Europe serves to depict the continent’s physical attributes, such as mountains, rivers, lakes, seas, and other natural landscapes. Also referred to as relief, topographic, or terrain maps, physical maps of Europe are crafted to furnish information about the continent’s landforms and physical features.
Distinctive Features of Physical Maps
A primary utility of a physical map of Europe lies in its ability to elucidate the continent’s geography. For instance, one can ascertain the location of prominent mountain ranges, including the Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathians, via a physical map. It also illustrates the placement of major rivers like the Danube, Rhine, and Volga, and lakes such as Lake Geneva and Lake Como. A physical map, therefore, enhances our comprehension of Europe’s topography and natural features.
Another striking characteristic of a physical map of Europe is its use of color and shading to signify elevation. Highlands and mountains are typically rendered in brown, whereas lowlands and valleys are depicted in shades of green or blue. Observing a physical map can provide insights into the relative altitudes of various areas, giving a sense of the terrain’s ruggedness or flatness. This information proves beneficial for planning outdoor activities like hiking or understanding the navigation challenges posed by different regions.
Contrasting Physical and Political Maps of Europe
Contrarily, a political map of Europe is designed to exhibit the continent’s political boundaries. It generally illustrates countries, states, provinces, and other administrative divisions, along with significant cities, roads, and other human-made features. Its primary goal is to offer insights into Europe’s political and administrative systems.
Political maps of Europe facilitate an understanding of the continent’s diverse countries and regions. For instance, such a map can reveal the borders of nations like France, Germany, and Spain, and pinpoint major cities like Paris, Berlin, and Madrid. Political maps can also identify the location of significant landmarks like the Eiffel Tower, the Colosseum, and the Brandenburg Gate.
Detailing: A Key Difference between Physical and Political Maps
Physical maps and political maps diverge in their focus—physical maps spotlight the land’s natural features, while political maps concentrate on human-made elements. Physical maps are instrumental in understanding Europe’s physical geography, whereas political maps elucidate Europe’s political geography.
Detailing is another distinguishing factor between physical and political maps. While physical maps often boast a high level of detail, featuring a myriad of features and landmarks, political maps may prioritize administrative boundaries and major cities over natural features.
Summarizing the Importance of Physical and Political Maps
In summation, physical maps of Europe are a valuable resource for grasping the continent’s natural geography. They pinpoint the location of various natural features, enhancing our understanding of the topography and terrain of different regions. On the other hand, political maps of Europe are designed to depict the continent’s political and administrative structures, such as countries, states, and cities. Both map types serve distinct purposes, and together, they offer a comprehensive understanding of Europe’s geography.
What’s New in Our Collection: Physical Map of Europe
Our collection now includes a “Physical Map of Europe.” It differs from a “Political Map of Europe” as it focuses on depicting physical structures or landforms, including lakes, mountains, seas, oceans, deserts, plains, forests, jungles, and grasslands. This topographical representation provides a more comprehensive view of the physical features one might encounter when traveling through the depicted country or continent.
Physical Map versus Topographical Map
However, it’s essential not to confuse a physical map of Europe with a topographical map of Europe. Although similar, they aren’t identical— a topographical map typically employs contour lines to indicate changes in the landscape, often related to altitude.
We now have a Europe Map for 2023. This is possibly the best and most easily read map of Europe